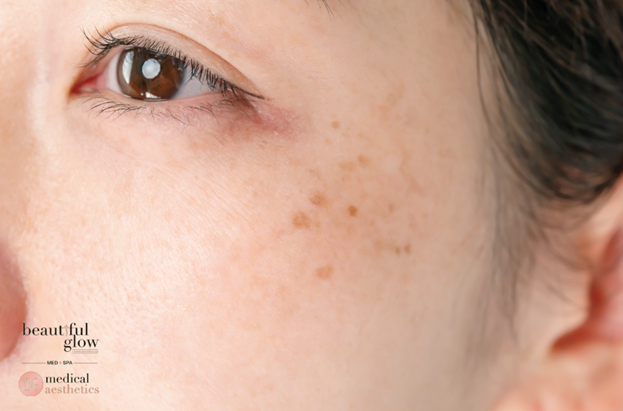
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is a medical term used to describe darker patches of skin from excess melanin production. This can be caused by acne scars and sun damage to hormone fluctuations and is a common skin condition.
- Face Acids: Whenever you exfoliate your skin, new skin cells emerge to take the place of old ones. The process helps even out your skin tone and makes it smoother overall. Popular options include:
- Alpha hydroxy Acids (such as glycolic, lactic, citric, malic, or tartaric acid
- Azelaic Acid
- Kojic Acid
- Salicylic Acid
- Vitamin C (in the form of L-Ascorbic Acid)
- Retinoids: It can come in either a prescription or OTC formula; however, OTC versions tend to be weaker. Derived from vitamin A, retinoids are among some of the oldest OTC skin care ingredients used.
- Chemical Peel: a chemical peel uses acids at stronger concentrations to treat the desired area of skin. They reduce the appearance of hyperpigmentation by removing the top layers of your skin (epidermis). Deeper versions may also penetrate the middle layer of your skin (dermis) to produce more dramatic results.
- Possible risks with both at-home and in-office chemical peels include:
- Redness
- Irritation
- Blistering
- Infection
- Scarring
- Allergic Reaction
- Chemical peels may not be the best treatment option if you are out in the sun on a regular basis. It may cause your skin to be more sensitive to the sun’s rays. If you do not adequately apply sunscreen and use other UV protection, the sun may worsen your hyperpigmentation. Extra precautions are needed for at least one week after your last chemical peel.
- Chemical peels may work if you have:
- Age Spots
- Sun Damage
- Melasma
- Blotchy Skin
- Possible risks with both at-home and in-office chemical peels include:
- Laser Peel (Skin Resurfacing): A laser peel (resurfacing) treatment uses targeted beams of light to reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Ablative lasers are the most intense, and they involve removing layers of your skin. It may cause more side effects.
- Non-ablative procedures target the dermis to promote collagen growth and tightening effects.
- Intense Pulse Light Therapy (IPL): It is a type of non-ablative (fractional) laser treatment and stimulates collagen growth within the dermis. This requires multiple sessions. IPL is used for overall pigmentation issues, but flat spots especially respond to this treatment. It may also help reduce the appearance of wrinkles, spider veins, and enlarged pores.
- Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is an in-office procedure used to treat hyperpigmentation that affects the epidermis only (superficial scarring).
- Dermabrasion: Dermabrasion involves the removal of your epidermis, but its effects continue down to a part of your dermis. It is sometimes used to smooth out wrinkles, the procedure has been historically used to address texture concerns. These include:
- Acne Scars
- Age Spots
- Chickenpox Scars
- Injury Scars
- Sun Damage
- Lightening Creams: Lightening creams are over-the-counter treatments that work with select ingredients to help decrease pigmentation. They are usually applied once or twice a day to help lighten the skin over time. Topical treatments for lightening also come in gel form, and common ingredients include:
- Licorice Extract
- Vitamin B3 (niacindamide)
What works best for each skin tone?
- The following might be off limits if you tan easily or have darker skin: High-Beam Lasers, IPL Therapy
- Medium skin tones may find the following options helpful: Chemical Peels, Microdermabrasion
- Darker skin might benefit from: Glycolic Acid, Kojic Acid, OTC Lightening Creams, Microdermabrasion, Lower-Strength Chemical Peels, Laser Treatments (at lower intensities over a larger number of sessions)
